Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
Description
You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Example 1:
Input:n = 2
Output:2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input:n = 3
Output:3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
Approach
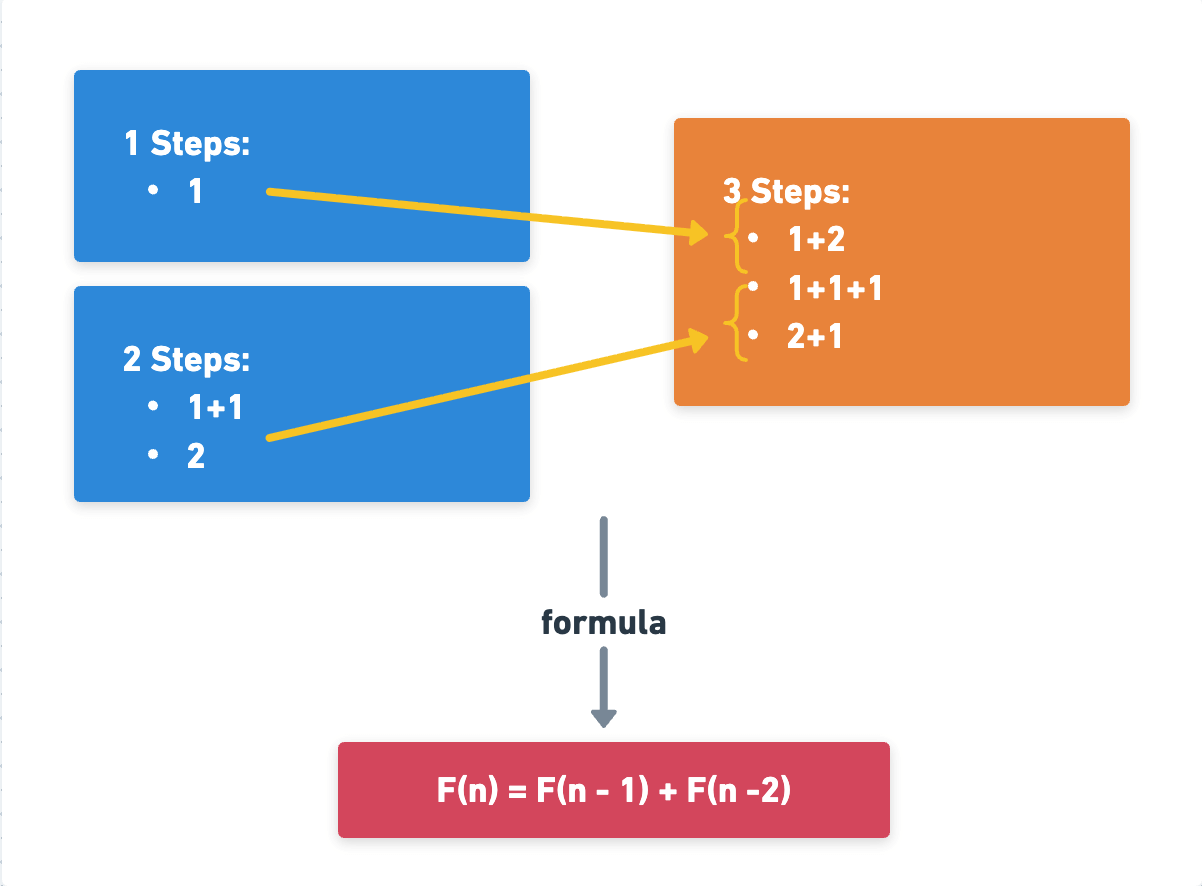
We can use a dynamic programming approach. The key observation is that to reach the i-th step, you could have come from either the (i-1)-th step (by taking a single step) or the (i-2)-th step (by taking a double step).
Therefore, the number of ways to reach the i-th step can be expressed as:
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var climbStairs = function (n) {
// numWaysToClimb[i] stores the number of ways to climb 'i' steps.
// Base cases: 0 steps (placeholder), 1 step (1 way), 2 steps (2 ways).
// numWaysToClimb[1]: 1 way to climb 1 step (take one 1-step).
// numWaysToClimb[2]: 2 ways to climb 2 steps (take two 1-steps: 1+1, or take one 2-step: 2).
const numWaysToClimb = [0, 1, 2];
// For each step 'i', the ways to reach it are the sum of ways to reach (i-1) and (i-2).
for (let i = numWaysToClimb.length; i <= n; i++) {
numWaysToClimb[i] = numWaysToClimb[i - 1] + numWaysToClimb[i - 2];
}
return numWaysToClimb[n];
};
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity is because we use a single loop that iterates up to n, calculating the number of ways to climb each step.
Space Complexity
The space complexity is due to the array numWaysToClimb that stores the number of ways to climb each step up to n.