Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
Description
There is a robot on an m x n grid. The robot is initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m - 1][n - 1]). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Given the two integers m and n, return the number of possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner.
The test cases are generated so that the answer will be less than or equal to .
Example 1:
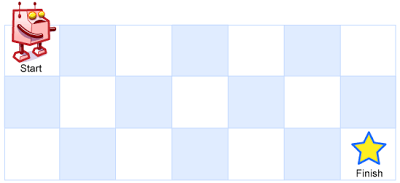
Input: m = 3, n = 7
Output: 28
Example 2:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation: From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
- Right -> Down -> Down
- Down -> Down -> Right
- Down -> Right -> Down
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 100
Approach
We can use a space-optimized dynamic programming approach: maintain a 1D array of length n (initialized to 1s) and process the grid row by row; for each cell update the current array entry to be the sum of its previous value (paths from above) and the value to its left (paths from left).
Solution
/**
* @param {number} m
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var uniquePaths = function (m, n) {
// results[j] will hold the number of ways to reach the current row's column j
const results = new Array(n).fill(1);
// Start from the second row (i = 1) because the first row is all 1 step
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
// For each column from the second (j = 1) to the last,
// accumulate paths from above (results[j]) and from left (results[j - 1])
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
results[j] += results[j - 1]; // ways_from_above + ways_from_left
}
}
// The last element contains the number of ways to reach bottom-right
return results[n - 1];
};
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity is since we iterate through each cell of the m x n grid once.
Space Complexity
The space complexity is due to the 1D array of size n used to store the number of unique paths to each column in the current row.