Table of Contents
Open Table of Contents
Description
Given two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively, return the median of the two sorted arrays.
The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
Output: 2.00000
Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
Output: 2.50000
Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
Constraints:
nums1.length == mnums2.length == n0 <= m <= 10000 <= n <= 10001 <= m + n <= 2000-10^6 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10^6
Approach
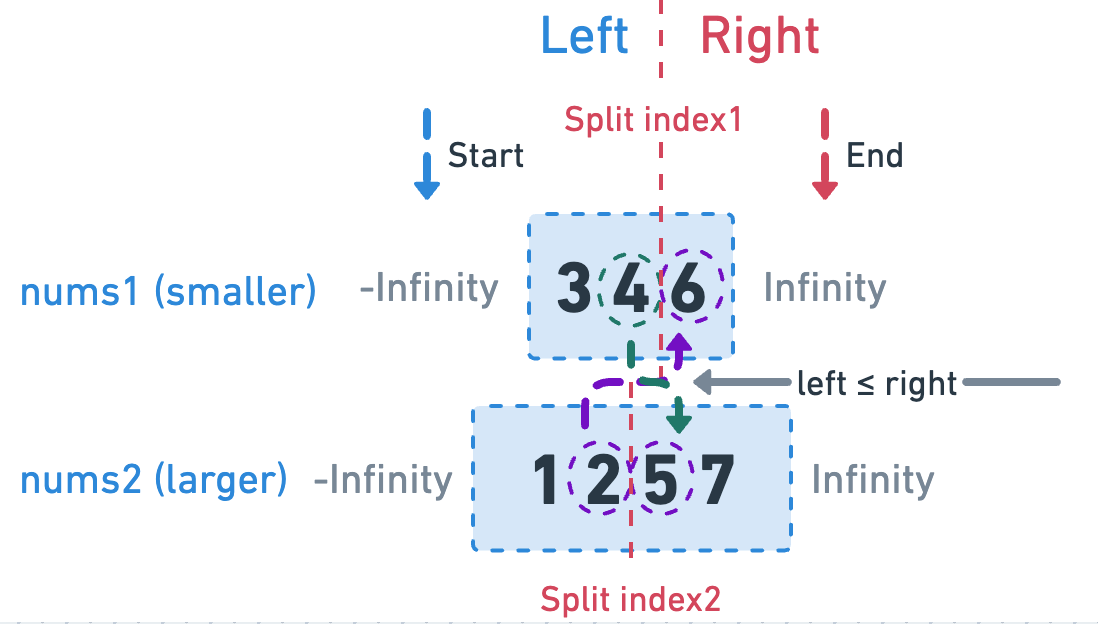
Since the description mentions that the complexity must be O(log(m+n)), we cannot traverse the array or create a new sorted array.
Therefore, the idea is to use binary search to find splitIndex1 and splitIndex2, which will divide nums1 and nums2 into left and right partitions, and satisfy the following rules:
- The number of elements in the left partition must be equal to the number in the right partition or right + 1 (for the median).
- The maximum value in the left partition must be less than or equal to the minimum value in the right partition (for a sorted array).
Solution
/**
* @param {number[]} nums1
* @param {number[]} nums2
* @return {number}
*/
var findMedianSortedArrays = function (nums1, nums2) {
// Ensure nums1 is the smaller array to simplify the binary search
if (nums1.length > nums2.length) {
[nums1, nums2] = [nums2, nums1];
}
const m = nums1.length,
n = nums2.length;
// Binary search over the smaller array
for (let start = 0, end = m; start <= end; ) {
// Calculate split indices for both arrays
let splitIndex1 = Math.ceil((start + end) / 2);
let splitIndex2 = Math.ceil((m + n) / 2) - splitIndex1;
// Handle edge cases for split indices going out of bounds
let num1Left = leftToInteger(nums1[splitIndex1 - 1]);
let num1Right = rightToInteger(nums1[splitIndex1]);
let num2Left = leftToInteger(nums2[splitIndex2 - 1]);
let num2Right = rightToInteger(nums2[splitIndex2]);
// Check if we have found the correct partition
if (num1Left <= num2Right && num2Left <= num1Right) {
// Check if the total number of elements is odd or even
return (m + n) % 2
? Math.max(num1Left, num2Left)
: (Math.max(num1Left, num2Left) + Math.min(num1Right, num2Right)) / 2;
}
// Adjust the binary search range
if (num2Left > num1Right) {
start = splitIndex1; // Move right in nums1
} else {
end = splitIndex1 - 1; // Move left in nums1
}
}
};
function leftToInteger(num) {
return isNaN(num) ? -Infinity : num;
}
function rightToInteger(num) {
return isNaN(num) ? Infinity : num;
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity is O(log(min(m, n))) because we perform a binary search over the smaller array.
Space Complexity
The space complexity is O(1) because we only use a constant amount of space.